-

“Revolutionizing LNG: Baker Hughes and Argent LNG’s Louisiana Mega-Project”
Baker Hughes’ Solution for New LNG Plant Baker Hughes has been selected by Argent LNG to supply liquefaction solutions, power generation equipment, and gas compression systems for their proposed LNG export facility in Louisiana. This collaboration underscores Baker Hughes’ commitment to delivering advanced LNG solutions and its strategic importance in the energy transition. The project,…
-
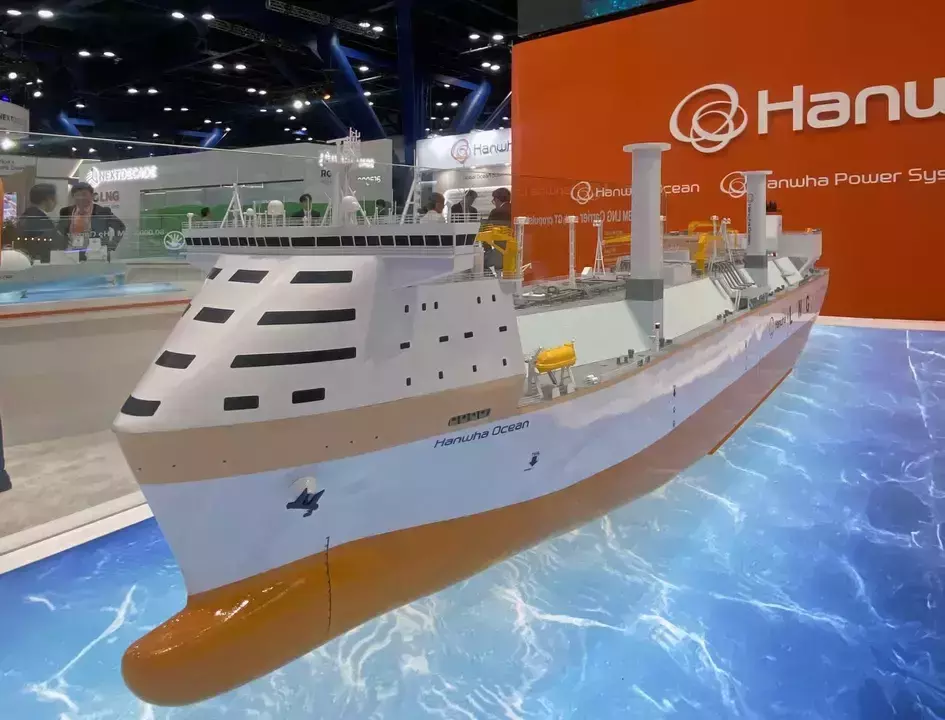

Revolutionizing Maritime Sustainability: Hanwha Ocean and Baker Hughes’ Ammonia Gas Turbine Innovation
Hanwha Ocean and Baker Hughes: Pioneering Carbon-Free Shipping with Ammonia Gas Turbines The recent partnership between South Korea’s Hanwha Ocean, Hanwha Power Systems, and energy technology firm Baker Hughes marks a pivotal moment in the maritime industry’s quest for carbon-free operations. This collaboration aims to develop a new small-size ammonia gas turbine, a groundbreaking innovation…
-
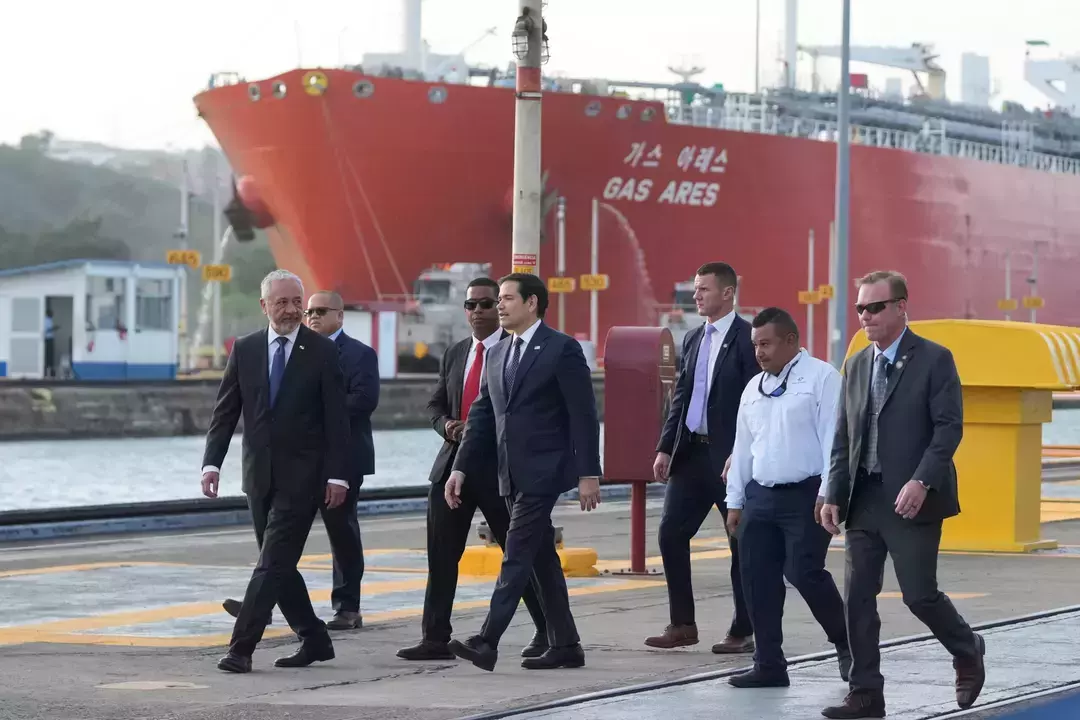

Rubio’s Ultimatum: U.S. Demands Panama Curb Chinese Influence Over Panama Canal
Rubio Calls Chinese Presence at Panama Canal ‘Unacceptable’ The topic of this article revolves around U.S. Secretary of State Marco Rubio’s visit to Panama and his strong criticism of China’s influence over the Panama Canal. Rubio’s visit was marked by his warning to Panama’s President Jose Raul Mulino that the U.S. would take measures if…
-
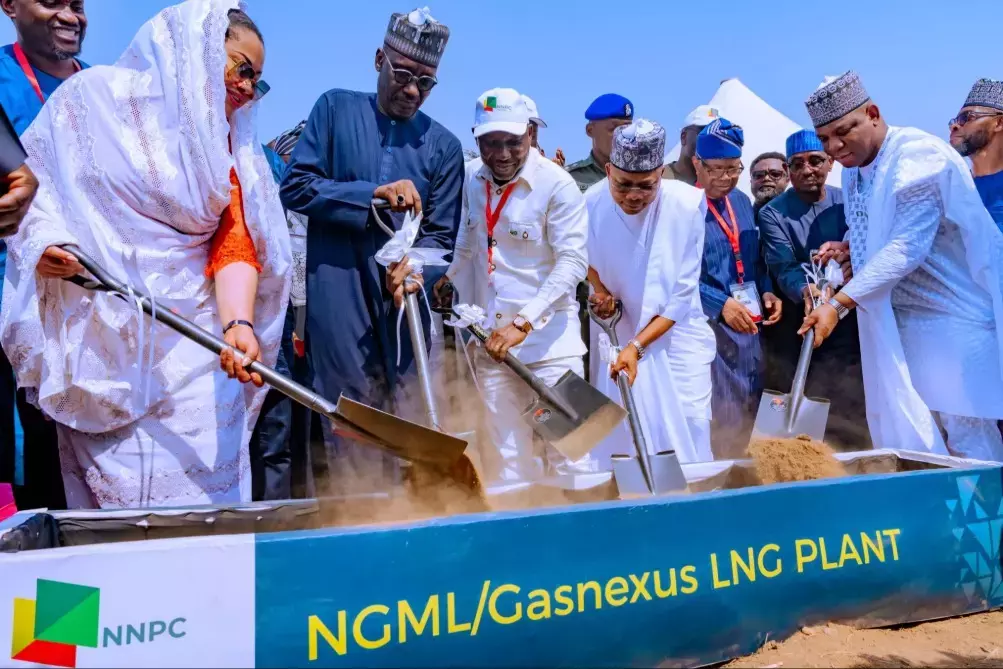

Nigeria’s Gas Revolution: Five Mini-LNG Plants Inaugurated to Drive Sustainable Energy and Economic Growth
Five Mini-LNG Plants Inaugurated in Nigeria: A Step Towards Sustainable Energy The Nigerian National Petroleum Corporation (NNPC) and its partners have launched five mini-LNG plants in Ajaokuta, Kogi State, with a combined capacity of 97 million standard cubic feet of gas per day (mmscf/d). This initiative is part of the federal government’s Gas Revolution Agenda,…
-
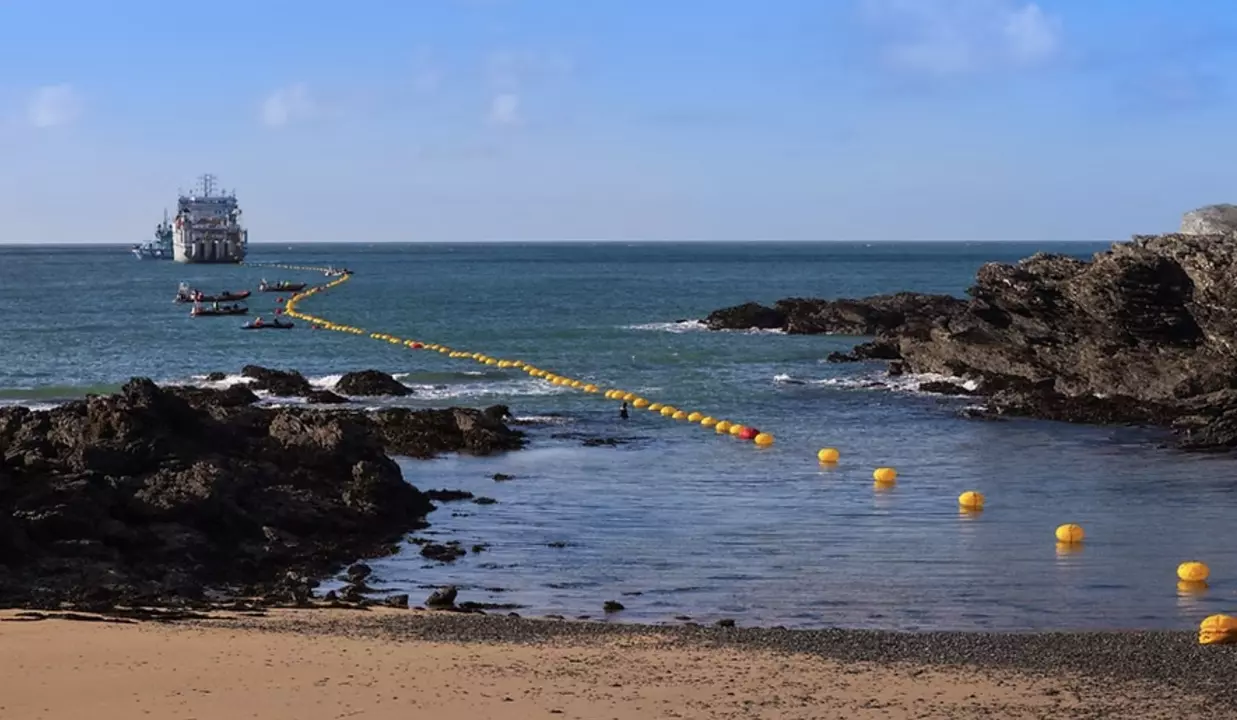

Greenlink Interconnector: Revolutionizing Energy Connectivity Between Ireland and Great Britain
Greenlink Interconnector: Pioneering Energy Connectivity between Ireland and Great Britain The Greenlink interconnector, a 504 MW high-voltage direct current (HVDC) link between Ireland and Great Britain, has recently begun commercial operations, marking a significant milestone in European energy infrastructure. This privately financed project operates under the Cap & Floor regulatory regimes in both countries, representing…
-

“Fueling Europe’s Green Future: The Danish-German Hydrogen Pipeline”
The Danish-German Hydrogen Pipeline: A Green Transition Catalyst The Danish government has unveiled ambitious initiatives to support the country’s emerging hydrogen market, committing to establish a Danish-German hydrogen pipeline by 2030. This project, funded at a billion-scale (DKK), aims to enhance energy security and facilitate the green transition in Europe. The government’s announcement highlights the…
NeonHorizon
Exploring the horizons of the maritime industry.