-
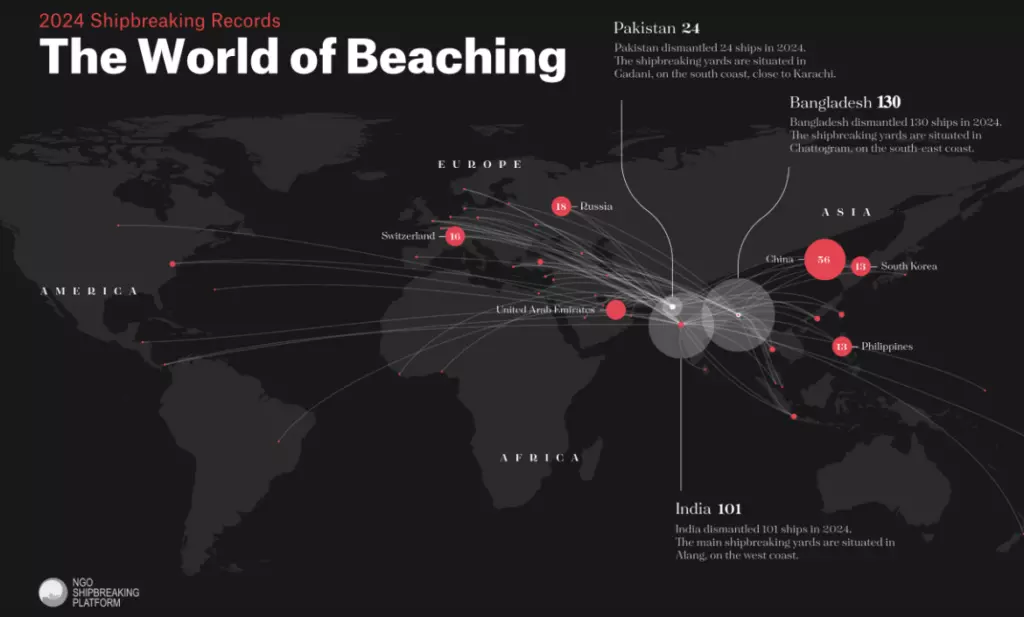
Alarming Practices in Shipbreaking: Environmental and Safety Challenges in South Asia
The Shipbreaking Industry: Environmental and Safety Concerns The shipbreaking industry faces significant environmental and safety challenges, with 80% of global vessel tonnage scrapped in 2024 dismantled under substandard conditions, primarily in South Asia. This article delves into alarming practices, focusing on Bangladesh, India, and Pakistan, and explores the regulatory frameworks, technological innovations, and future prospects…
-

Navigating Sustainability: CLdN’s Pooling Incentive for FuelEU Maritime Compliance
The FuelEU Maritime Directive and CLdN’s Pooling Incentive The FuelEU Maritime (FEUM) directive is a pivotal initiative aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions in the maritime sector by promoting the use of renewable and low-carbon fuels. However, the higher costs of biofuels pose significant challenges. CLdN has introduced a pooling incentive to provide flexibility for…
-
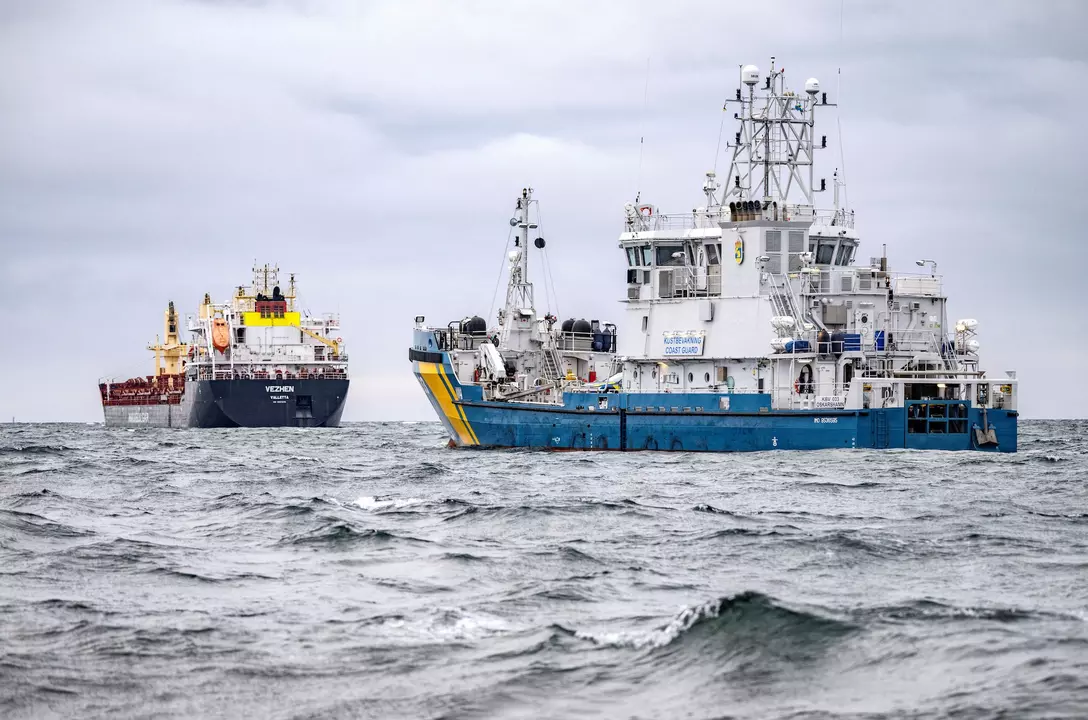

“Baltic Sea Cable Cut: Accidental Damage Exposes Regional Vulnerabilities”
Sweden Says Ship Broke Baltic Sea Cable by Accident Incident Overview On January 26, 2025, the cargo ship Vezhen, sailing under the Maltese flag, encountered severe weather conditions in the Baltic Sea. En route from Sweden to Latvia, the vessel accidentally dropped its anchor, severing a critical subsea cable that connects the two countries. Initial…
-
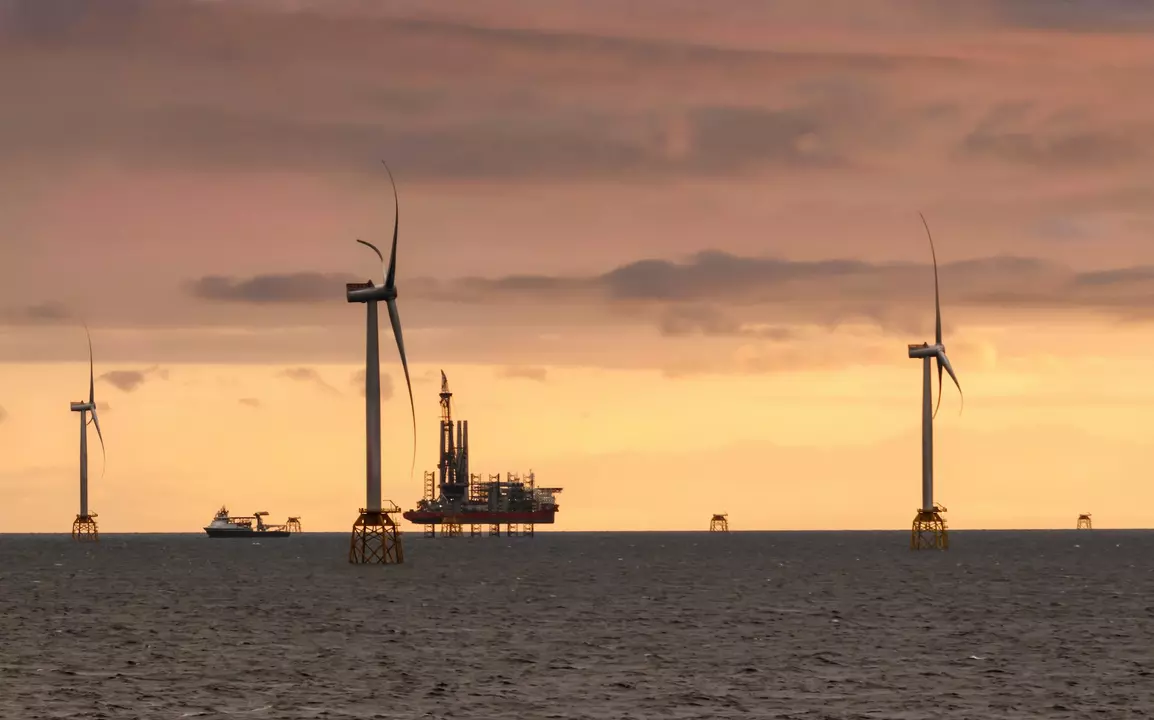

Navigating Uncertainty: New Jersey’s Offshore Wind Challenges and Future Prospects
New Jersey’s Offshore Wind Solicitation Cancellation: Challenges and Future Prospects Introduction to New Jersey’s Offshore Wind Solicitation Cancellation The New Jersey Board of Public Utilities (BPU) recently canceled its fourth offshore wind solicitation, signaling a significant shift in the state’s renewable energy development strategy. This decision was prompted by Shell’s withdrawal from the Atlantic Shores…
-

“India’s Maritime Development Fund: Charting a Course for Global Maritime Leadership”
Introduction to India’s Maritime Development Fund The establishment of India’s Maritime Development Fund marks a significant milestone in the nation’s maritime journey. Announced recently during the Union Budget, the fund has a corpus of approximately ₹25,000 crore (about $3 billion) [Source: Reuters]. The primary objective of this fund is to provide long-term financing for the…
-
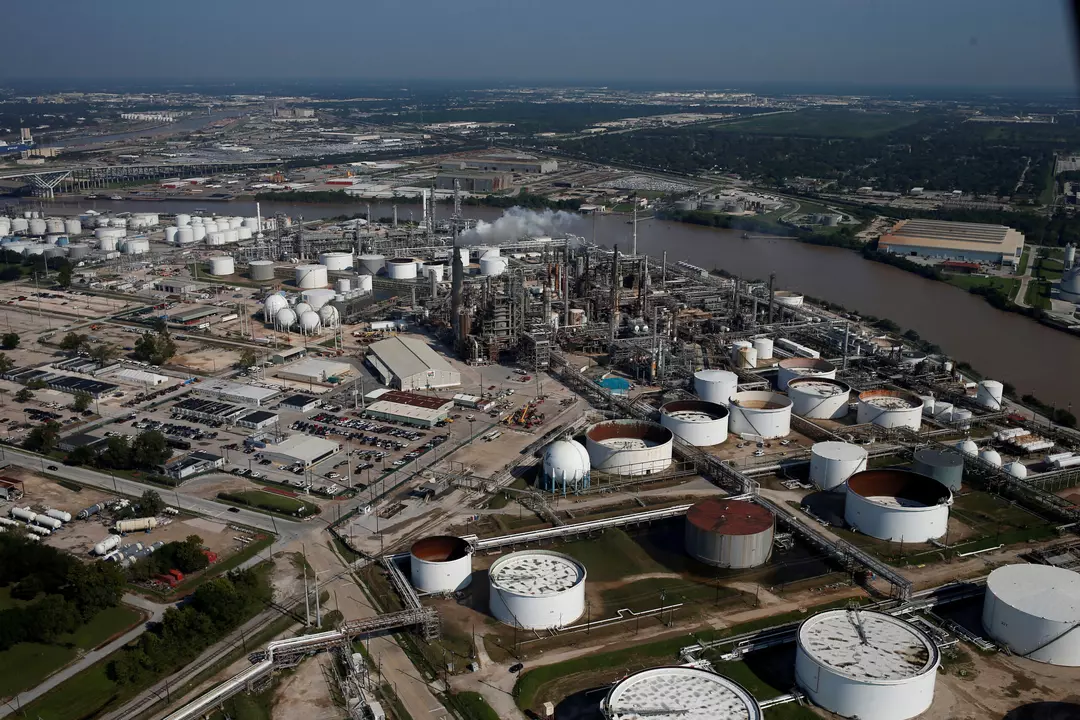

Trump’s Oil Tariffs: Reshaping Global Oil Markets and Refining Dynamics
Introduction to Trump’s Oil Tariffs On February 1, 2025, U.S. President Donald Trump imposed a series of trade tariffs targeting oil imports from Canada and Mexico, with rates reaching as high as 25%. This decision forms part of a broader strategy to protect U.S. interests by addressing national emergencies such as fentanyl trafficking and illegal…
-
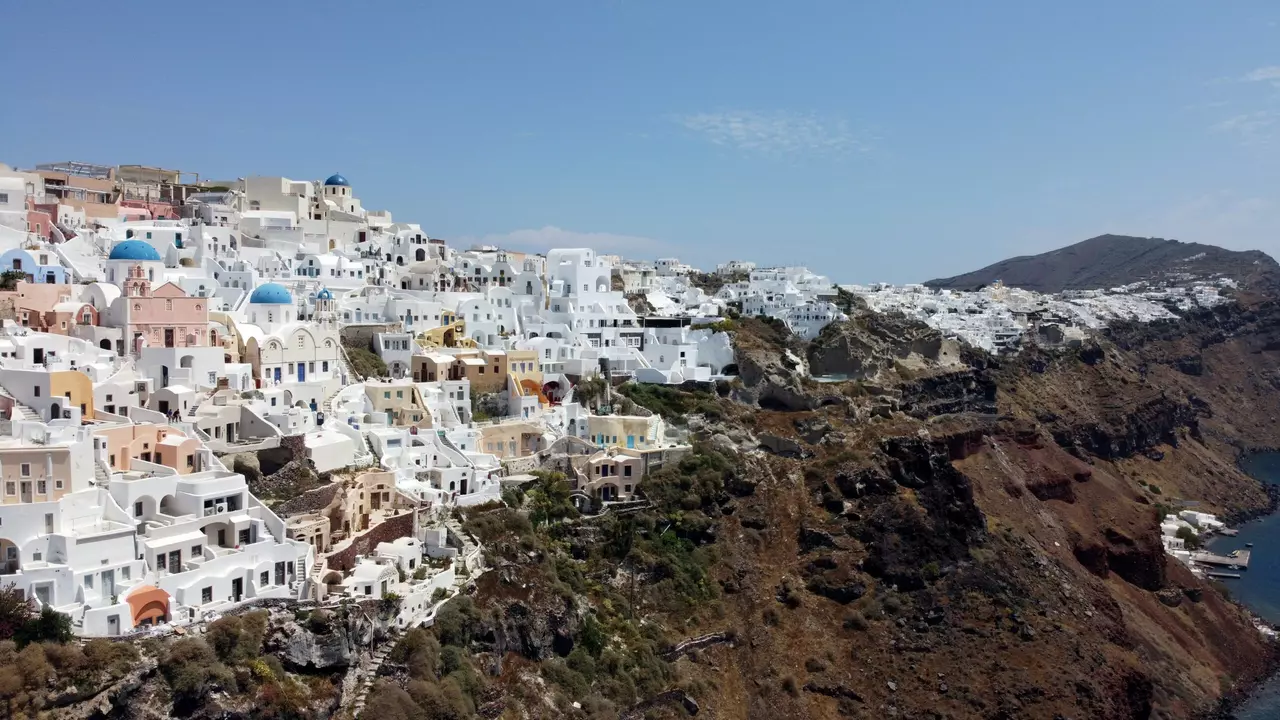

Santorini Shaken: Seismic Surges Threaten Tourism Paradise
Seismic Activity Around Santorini: Implications for Tourism Greece’s tourism industry is on high alert after recent seismic activity around the Aegean tourist island of Santorini. Greek authorities have issued warnings and implemented precautionary measures to safeguard visitors and residents. This article delves into the geological context, current situation, precautionary measures, and the potential impact on…
NeonHorizon
Exploring the horizons of the maritime industry.



