2024: A Pivotal Year for Climate Change and the Maritime Industry
The year 2024 has been confirmed by the Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S) as the warmest on record globally. This alarming trend has significant implications for the maritime industry, which is particularly vulnerable to changes in sea surface temperature (SST), sea ice extent, and extreme weather events.
Record-Breaking Temperatures and Their Impacts
Global Temperature Trends
According to C3S, 2024 was the first calendar year where the average global temperature exceeded 1.5°C above its pre-industrial level. This is a stark reminder of the ongoing climate change, driven primarily by human activities. The El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO) also contributed to the unusual temperatures observed during the year.
Maritime Industry Implications
The maritime industry is already feeling the effects of these temperature increases. Rising sea surface temperatures can lead to:
- Increased heat stress for seafarers, impacting their health and productivity.
- Changes in marine ecosystems, affecting fisheries and aquaculture.
- Altered ocean currents, which can influence shipping routes and port operations.
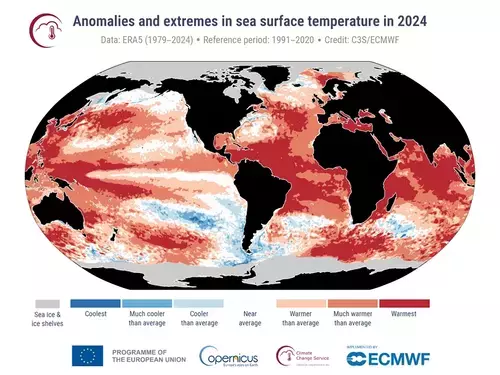
Sea Surface Temperature and Sea Ice Extent
Record-High Sea Surface Temperatures
In 2024, the annual average sea surface temperature over the extra-polar ocean reached a record high of 20.87°C. This was 0.51°C above the 1991–2020 average. The impacts of such high temperatures on the maritime industry include:
- Increased corrosion rates on ships due to warmer waters.
- Potential shifts in marine life, affecting biodiversity and fisheries.
- Changes in water density, which can impact vessel draft and navigation.
Declining Sea Ice Extent
Around Antarctica, sea ice extent reached record or near-record low values during a large part of 2024. In the Arctic, the sea ice extent fell well below average in the latter part of the year. The maritime industry must adapt to these changes, as they can open new shipping routes but also pose challenges such as:
- Increased risks of navigating in icy waters.
- Potential environmental impacts on polar regions due to increased maritime activity.
Atmospheric Concentrations of Greenhouse Gases
The atmospheric concentrations of carbon dioxide and methane continued to increase and reached record annual levels in 2024. These greenhouse gases contribute to global warming and have indirect effects on the maritime industry, including:
- Rising sea levels, which can impact port infrastructure and coastal shipping routes.
- Increased frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, affecting maritime operations and safety.
Conclusion
The year 2024 has set alarming records in global temperature, sea surface temperature, and sea ice extent. These changes have profound implications for the maritime industry, requiring urgent adaptation and mitigation strategies. As Carlo Buontempo, Director of the Copernicus Climate Change Service, emphasized, swift and decisive action can still alter the trajectory of our future climate. The maritime industry must play its part in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and adapting to the challenges posed by climate change.
References
Data and insights for this article were provided by renowned organizations involved in global climate monitoring, including the ECMWF, NASA, NOAA, the UK Met Office, Berkeley Earth, and the World Meteorological Organisation (WMO). Their coordinated efforts highlight the exceptional conditions experienced during 2024 and underscore the urgency of addressing climate change.
Sources:
- 2024 was hottest year on record and first to exceed 1.5C warming
- WMO confirms 2024 was hottest year on record – The Jerusalem Post
- Taiwan says 2024 was hottest year on record | National | carrollspaper.com
- WMO confirms 2024 was hottest year on record – AOL
- 2024 was hottest year on record: Weather agencies
- Taiwan says 2024 was hottest year on record – indexjournal.com
- 2024 Was Hottest Year On Record For Norway’s Arctic
- Taiwan says 2024 was hottest year on record | National …
- 2024 was hottest year on record say experts – BBC Newsround
- Taiwan says 2024 was hottest year on record | National News | messenger …

Leave a Reply