Petrobras’ Strategic Divestment of the Tartaruga Field: A Comprehensive Analysis
Introduction to Petrobras’ Divestment Strategy
Petrobras, Brazil’s state-controlled oil giant, has been actively pursuing a divestment strategy to optimize its portfolio and focus on core assets. This strategy aligns with the company’s broader goals of reducing debt, improving operational efficiency, and enhancing shareholder value. Recent divestment initiatives include the sale of non-core assets, particularly in shallow water fields, to concentrate on deepwater and ultra-deepwater exploration and production. The Tartaruga field, located in the Sergipe-Alagoas Basin, is one such asset that Petrobras has targeted for divestment.
The Tartaruga field divestment is significant as it represents Petrobras’ commitment to streamlining its operations and reallocating resources to more profitable ventures. The field, which has been in production since 2013, has contributed to Petrobras’ overall output, but its shallow water nature makes it less aligned with the company’s strategic focus on deepwater assets. By divesting its 25% stake in the Tartaruga field, Petrobras aims to reduce operational costs and focus on more lucrative projects, such as those in the pre-salt layer.
This move is part of a larger trend within Petrobras to optimize its asset portfolio. The company has been divesting from refineries, onshore fields, and other non-core assets to concentrate on its strengths in deepwater exploration. The Tartaruga field divestment is a clear example of this strategy in action, as it allows Petrobras to reallocate capital to more promising projects while maintaining its position as a leading player in the global oil and gas industry.
According to recent reports, the sale process for the Tartaruga field is being conducted in line with Petrobras’ divestment guidelines and complies with Decree 9,355/2018, which governs special procedures for the assignment of exploration, development, and production rights. This ensures that the divestment is carried out transparently and in accordance with regulatory requirements, further solidifying Petrobras’ commitment to good governance and operational excellence.
Detailed Analysis of the Tartaruga Field
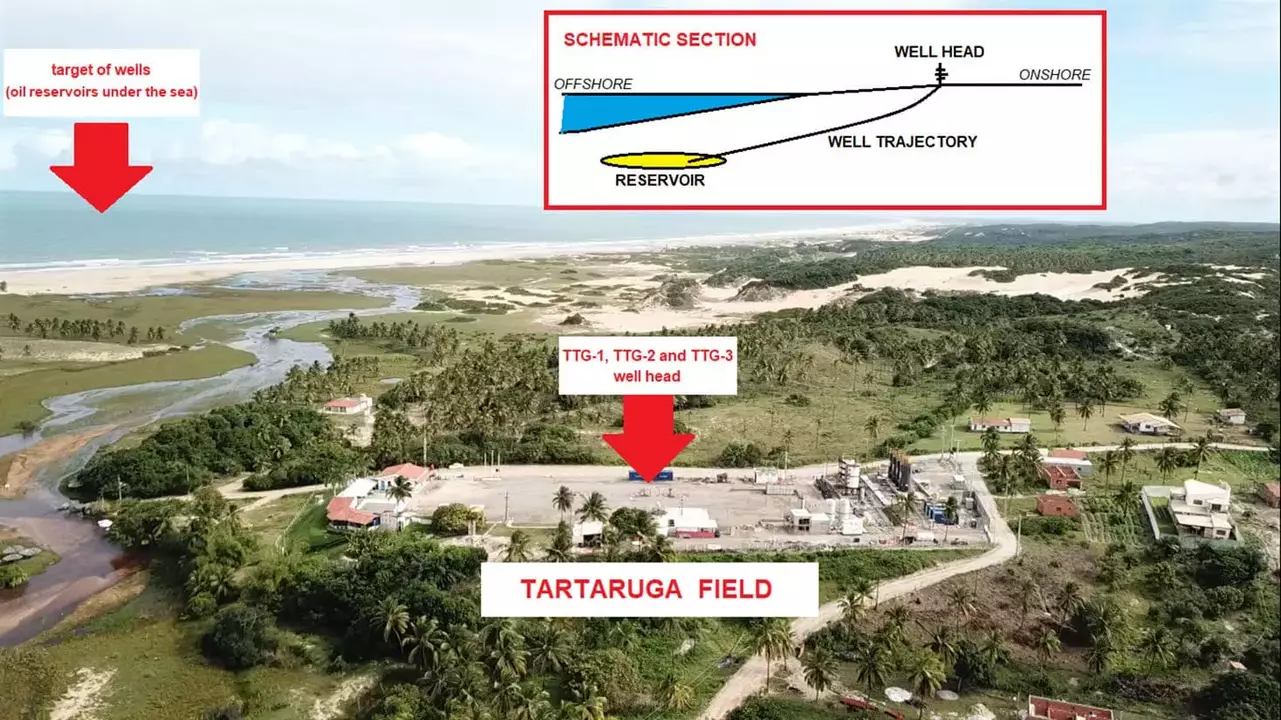
The Tartaruga field, located in the Sergipe-Alagoas Basin off the coast of Brazil, is a significant shallow-water oil and gas field operated by Petrobras. Geologically, the field is situated in a region known for its prolific hydrocarbon reserves, characterized by sedimentary formations that have proven to be highly productive. The field’s location in the shallow waters of the basin allows for relatively easier access and lower operational costs compared to deepwater fields, making it an attractive asset in Petrobras’ portfolio.
Historically, the Tartaruga field has been a steady contributor to Petrobras’ production. The field’s production history dates back to its discovery and subsequent development, with consistent output over the years. Currently, the field produces approximately 25,000 barrels of oil equivalent per day (boe/d), contributing to Petrobras’ overall production targets. The field’s infrastructure includes production platforms and pipelines that facilitate the efficient transport of hydrocarbons to onshore facilities.
Petrobras’ divestment strategy, which includes the sale of a 25% stake in the Tartaruga field, aligns with its broader goal of portfolio optimization and capital allocation. The sale is part of a binding phase, as reported by Yahoo Finance, and is expected to attract significant interest from investors. This divestment allows Petrobras to focus on its core deepwater assets while still maintaining a majority stake in the Tartaruga field, ensuring continued revenue generation.
The synergies between the Tartaruga field and Petrobras’ portfolio are evident in the company’s ability to leverage existing infrastructure and expertise in the region. The field’s production complements Petrobras’ broader operations in the Sergipe-Alagoas Basin, where the company has a strong presence. Additionally, the divestment aligns with Petrobras’ strategic plan to reduce debt and improve profitability, as highlighted in its 2024-2028 Strategic Plan. By optimizing its portfolio, Petrobras aims to maximize value and ensure sustainable growth, with the Tartaruga field playing a key role in this strategy.
Petrobras’ Business Plan and Strategic Alignment
Petrobras’ 2025-2029 Business Plan outlines a strategic focus on optimizing its portfolio and maximizing value through targeted investments and divestments. The plan emphasizes the importance of concentrating resources on high-potential assets, particularly in deepwater exploration, while divesting non-core and less profitable ventures. This approach aligns with the company’s broader objective of reducing debt and enhancing profitability.
In the state of Sergipe, Petrobras has prioritized investments in the Sergipe-Alagoas Basin, a region known for its significant oil and gas reserves. The Tartaruga field, located in this basin, has been a focal point of these efforts. However, the decision to divest a 25% stake in the Tartaruga field is part of a strategic realignment aimed at streamlining operations and focusing on more lucrative projects. According to Offshore Energy, this divestment is in line with Petrobras’ strategy to optimize its portfolio and comply with regulatory requirements.
The strategic rationale behind the Tartaruga field divestment is multifaceted. Firstly, it allows Petrobras to reallocate capital to more profitable ventures, particularly in deepwater fields. Secondly, it aligns with the company’s goal of reducing operational complexity and focusing on core assets. As noted by Yahoo Finance, the divestment process is being conducted in accordance with Decree 9,355/2018, which governs special procedures for asset sales. This move not only strengthens Petrobras’ financial position but also enhances its ability to invest in future growth opportunities.
Impact on Petrobras’ Operations and Workforce
The divestment of the Tartaruga field by Petrobras has significant operational implications, particularly in terms of regional activities and workforce dynamics. The Tartaruga field, located in the Sergipe-Alagoas Basin, has been a key asset in Petrobras’ portfolio, contributing to the company’s overall production capacity. The divestment aligns with Petrobras’ broader strategy to focus on deepwater exploration and reduce its debt, as highlighted in its 2024-2028 Strategic Plan [Strategic Plan: what guides our decisions].
Operationally, the sale of the Tartaruga field could lead to a reallocation of resources within Petrobras. The company may redirect investments towards more profitable deepwater projects, which are central to its long-term strategy. This shift could result in a reduction of activities in the Sergipe-Alagoas Basin, impacting local suppliers and service providers who have been dependent on the Tartaruga field operations [Petrobras launches divestment of shallow water oil & gas field offshore Brazil].
The workforce impact is another critical aspect of this divestment. Petrobras has historically been a major employer in the region, and the sale of the Tartaruga field could lead to job reductions or reassignments. However, the company has emphasized that it will manage the transition responsibly, ensuring that affected employees are either redeployed to other projects or provided with adequate support [Petrobras begins divestment of Tartaruga shallow water field].
Despite the potential disruptions, the divestment also presents benefits. By shedding non-core assets, Petrobras can streamline its operations and focus on high-value projects, which could enhance overall efficiency and profitability. Additionally, the sale could attract new investments to the region, as the new operator may bring in fresh capital and expertise, potentially revitalizing local economic activities [Petrobras Eyes Minority Stake Sale in Shallow Water Field Off Brazil].
In conclusion, while the divestment of the Tartaruga field poses challenges, it also offers opportunities for Petrobras to optimize its portfolio and strengthen its financial position. The key will be managing the transition in a way that minimizes negative impacts on the workforce and regional economy while maximizing the strategic benefits of the divestment.
Conclusion and Future Prospects
The analysis of Petrobras’ strategic divestment of the Tartaruga field reveals several key findings. The Tartaruga field, located in the Sergipe-Alagoas Basin, has been a significant asset in Petrobras’ portfolio, contributing to the company’s production and revenue streams. The divestment process aligns with Petrobras’ broader strategy to focus on deepwater and ultra-deepwater assets, which are considered more profitable and aligned with the company’s long-term goals. The sale of a 25% stake in the Tartaruga field is part of this strategic shift, aimed at optimizing the portfolio and improving capital allocation.
Looking ahead, Petrobras is expected to continue its divestment strategy, focusing on non-core assets to reduce debt and reinvest in high-potential projects. The oil and gas industry, particularly in Brazil, is poised for growth, with increasing investments in exploration and production. Petrobras’ strategic plan for 2024-2028+ emphasizes the importance of maximizing value from its portfolio, with a significant portion of capital expenditure allocated to exploration and production activities. This focus is expected to drive future growth and enhance Petrobras’ competitive position in the global market.
For stakeholders, the divestment of the Tartaruga field presents both opportunities and challenges. Investors should consider the potential for increased returns from Petrobras’ streamlined portfolio, while also being mindful of the risks associated with the transition. Regulatory bodies and industry partners must ensure that the divestment process is conducted transparently and in compliance with legal frameworks. Overall, the strategic divestment of the Tartaruga field underscores Petrobras’ commitment to financial discipline and long-term value creation, positioning the company for sustained success in the evolving energy landscape.
Sources
- Yahoo Finance – Petrobras Begins Binding Phase for Sale of Tartaruga Field
- Offshore Energy – Petrobras Starts the Divestment Ball Rolling for Brazil’s Shallow Water Oil & Gas Field
- Petrobras – Strategic Plan: What Guides Our Decisions
- Offshore Energy – Petrobras Launches Divestment of Shallow Water Oil & Gas Field Offshore Brazil
- OilNow – Petrobras Begins Divestment of Tartaruga Shallow Water Field
- OE Digital – Petrobras Eyes Minority Stake Sale in Shallow Water Field Off Brazil

Leave a Reply